Introduction

Antimony is a potentially toxic and carcinogenic metalloid element in nature. It exists in the form of various antimony minerals. There are as many as 120 known antimony-containing minerals. Only minerals containing more than 20% of antimony have industrial value, and there are only more than 10 kinds.
Physical properties of antimony

Antimony is a gray metal element with a metallic luster. It exists in solid form at room temperature and generally exists in a silver-gray or silver-white rhombus crystal structure. Antimony has a large specific gravity, but poor electrical and thermal conductivity. The melting point, boiling point and density of antimony are 631℃, 1587℃ and 6.68g/cm³ respectively. It is a soft metal with a hardness of about 3. Antimony also has unique characteristics of thermal contraction and cold expansion and a decrease in resistivity with increasing temperature.
Chemical properties of antimony

The chemical symbol of antimony is Sb. It does not have reducing properties itself, but antimony compounds have reducing properties, which is between metals and non-metals.
Antimony is not easily oxidized in an environment below 250℃ and is a relatively stable metal. Antimony will release hydrogen from water when it is in a molten state at 700-800℃. Antimony is insoluble in water, dilute hydrochloric acid and concentrated hydrofluoric acid, but soluble in concentrated hydrochloric acid, concentrated sulfuric acid and concentrated nitric acid. Antimony reacts with halogen elements at room temperature to form halides, and can also react with non-metals such as nitrogen, sulfur and carbon.
Uses of antimony

Industrial field
Antimony compounds are flame retardant and are important raw materials for making flame retardants, especially in industries such as plastics, rubber and textiles, which can effectively improve the flame retardant properties of materials and reduce fire risks. Because antimony has good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, it is often used to make various alloys. Lead antimony alloys are used to make battery plates, while tin antimony alloys are needed to make welding materials and fuses.
Electronic industry
Antimony is mainly used to make electronic tubes, semiconductors, optoelectronic devices, etc. Antimony elements can improve the electrical conductivity and thermal stability of materials and perform well in electronic products.
Chemical industry
Antimony is mainly used in the chemical industry to produce antimony oxide, redox catalysts, plastic flame retardants, etc. Antimony compounds can increase the stability and flame retardancy of materials and are a very important chemical raw material.
Cosmetic industry
Antimony is widely used in the cosmetic industry because of its good adsorption and tenderness to the skin. Antimony compounds are widely used in cosmetics and skin care products, such as lipstick, eye shadow and facial powder.
Pharmaceutical industry
Antimony is often used to produce drugs for the treatment of diseases such as malaria, parasitic infections and anti-inflammatory diseases. It has broad-spectrum antibacterial, antiprotozoal and anti-tumor properties and is an important drug raw material.
Aviation field
Antimony can improve the strength and heat resistance of materials. It is often used in the production of high-temperature alloys, coatings, glass, etc. in aviation manufacturing and performs well in aviation manufacturing.
Metallurgical industry
Antimony can be used to purify metals and produce alloys. Antimony alloys have good mechanical strength, corrosion resistance and plasticity and are an important metallurgical raw material.
Ceramic industry
Antimony oxides and sulfides can be used to manufacture ceramic magneto-optical recording materials and are also important in ceramic materials. The hybrid system of antimony silicate and silver antimony silicate is also used to study transparent conductive ceramics.
Gunpowder materials
Antimony compounds are often used to make gunpowder. Their restraining shells absorb oxygen in the atmosphere, reducing smoke during combustion. They are one of the common raw materials for making Red Star gunpowder.
Antimony ore flotation beneficiation process
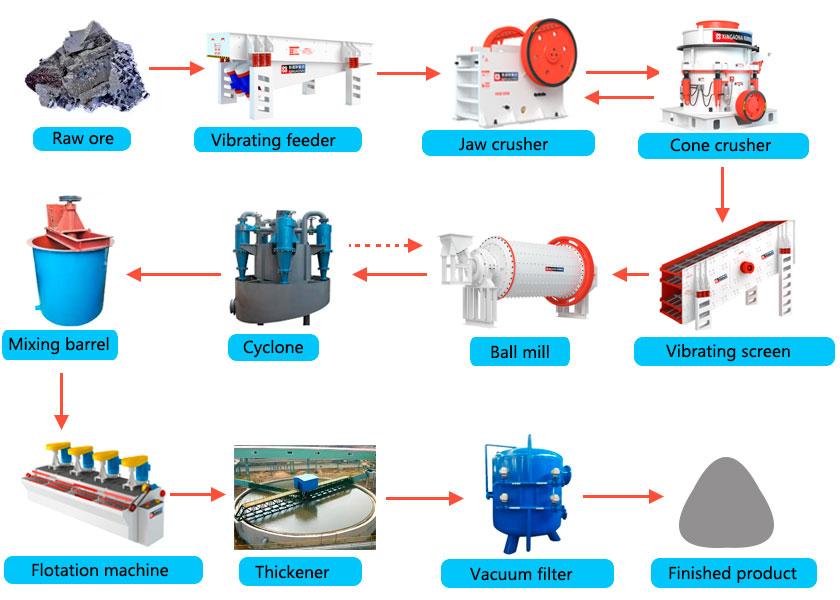
Before flotation beneficiation, the antimony ore must undergo two stages of treatment. The first is the crushing process, which is generally carried out in a two-stage open-circuit crushing method. The feeder and two jaw crushers are used to crush the minerals coarsely and finely. The crushed antimony ore is sent to the next stage of the process through a belt conveyor; the second is the grinding and classification process, which is also the main preparation stage before beneficiation. Generally, a closed-circuit grinding and classification process is adopted. The antimony ore and water are sent to the antimony ore ball mill in a certain proportion for wet grinding, and then graded by a spiral classifier. The grinding fineness is to a certain mesh number, and those that do not meet the requirements are returned to the ball mill for re-grinding. These two stages are the two major processes before the antimony ore floats.
The main process of mineral processing is the flotation stage, which mainly uses a flotation machine for a rough selection, and then adds reagents for four fine selections to select antimony concentrate. This process is a key stage and the main process in the antimony ore beneficiation production line; finally, the concentrate must be dehydrated for a second time, generally using a concentrator. The antimony concentrate foam from the floatation is fed into the concentrator through a slurry pump for primary dehydration, and then flows to the filter for secondary dehydration, and finally dehydrated to select antimony concentrate. For the treatment of its tailings, users can recycle it.(xingaonai)
Comments on “The use of antimony and the process of antimony ore dressing”